Ensuring Quality Through Cleaning Validation Software in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing

Maintaining cleanliness and hygiene in pharmaceutical manufacturing is crucial for ensuring product safety and quality, with patient well-being as the top priority. Cleaning validation plays a key role in confirming thorough cleansing of equipment and facilities to prevent cross-contamination and meet regulatory standards. Traditionally, this process relied on manual methods, which were complex and time-consuming. However, the introduction of cleaning validation software has revolutionized this practice by automating protocol creation, data analysis, and reporting. These software solutions, with their advanced algorithms and data management capabilities, enhance efficiency, accuracy, and compliance in cleaning validation activities. This article explores the significance of cleaning validation software and its role in helping businesses adhere to cleaning protocols and regulatory information.
Importance of Cleaning Validation Software
Cleaning validation software offers several key benefits for pharmaceutical manufacturing:
Efficient Protocol Creation: Software simplifies the creation of cleaning protocols, ensuring consistency and adherence to regulatory standards.
Real-time Monitoring and Data Collection: Manufacturers can monitor cleaning processes in real-time, detecting deviations promptly to prevent quality issues.
Data Analysis and Trending: Advanced analytics enable comprehensive analysis of historical data, identifying areas for improvement and optimizing cleaning processes.
Documentation and Reporting: Software facilitates centralized document management and automated report generation, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Integration with Enterprise Systems: Integration with other systems enhances workflow efficiency and data integrity across departments, supporting a culture of quality and compliance.
Regulatory Compliance: Cleaning validation software incorporates relevant regulatory guidelines, aiding manufacturers in meeting compliance standards during inspections and audits.
Cleaning Validation Guidelines and Protocols
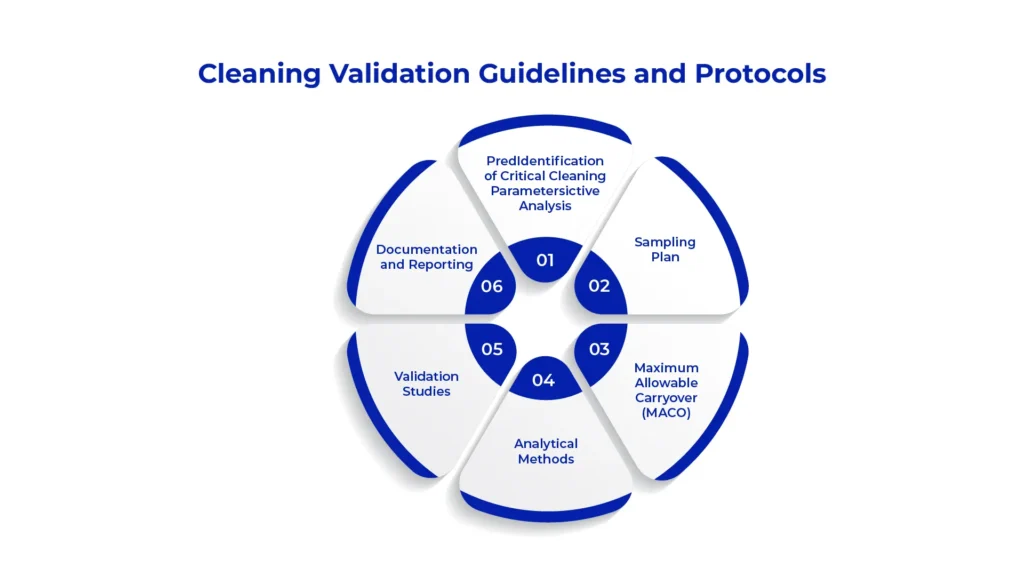
Cleaning validation guidelines and protocols are crucial for ensuring pharmaceutical manufacturing processes’ cleanliness and safety. They outline regulatory requirements from bodies like the US FDA and ICH, providing detailed instructions for validation studies, acceptance criteria, and documentation to comply with cGMP. These protocols specify steps and parameters for validating cleaning procedures, including sampling methods and residual level criteria. By adhering to these cleaning validation guidelines, manufacturers demonstrate process effectiveness, mitigate cross-contamination risks, and uphold product quality and patient safety standards.
Best Industry for Preventive and Calibration Management
Identification of Critical Cleaning Parameters: This includes identifying critical equipment surfaces, residues of concern, cleaning agents, cleaning methods, and acceptance criteria based on product and process characteristics.
Sampling Plan: Determining the locations and frequency of sampling to ensure representative samples are collected for analysis. This may involve swabbing, rinsing, or visual inspection of equipment surfaces.
Maximum Allowable Carryover (MACO): Utilizes MACO calculation to ascertain acceptable residue levels post-cleaning. MACO represents the maximum residue allowable between batches without compromising subsequent product safety or efficacy.
Analytical Methods: Selecting appropriate analytical methods for detecting and quantifying residues, such as High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Total Organic Carbon (TOC) analysis, or specific assays for active ingredients.
Validation Studies: Conducting validation studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of cleaning procedures. This involves performing cleaning trials using worst-case scenarios, such as maximum batch size or minimum acceptable cleaning time.
Documentation and Reporting: Comprehensive documentation of all cleaning validation activities, including protocols, results, deviations, and conclusions. A final cleaning validation report summarizes the findings and provides evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Information
Regulatory agencies provide guidelines and requirements for cleaning validation in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The lifesciences industry has to follow regulatory information in order to ensure expectant product quality. Some key regulatory documents that form the basis of regulatory information for the pharmaceutical sector include:
The FDA Guidance for Industry: The US FDA’s Cleaning Validation Guidelines detail regulatory expectations for effective cleaning in pharmaceutical manufacturing. They offer instructions for validation studies, acceptance criteria, and documentation, ensuring compliance with cGMP regulations. Adherence to the cleaning validation guidelines as per US FDA is critical for maintaining product quality and patient safety, aligning with regulatory standards throughout the manufacturing process.
The PDA Technical Report No. 29 emphasizes the importance of establishing scientifically sound and risk-based cleaning processes to ensure product quality and patient safety. Key aspects include selecting appropriate cleaning agents, defining acceptance criteria, validating cleaning procedures, and implementing robust monitoring systems. Adherence to these guidelines helps pharmaceutical manufacturers meet regulatory requirements and maintain the efficacy and integrity of their products.
The EMA Guideline on Setting Health Based Exposure Limits for Use in Risk Identification in the Manufacture of Different Medicinal Products in Shared Facilities offers detailed guidance on establishing health-based exposure limits for cleaning validation purposes. By setting these limits, manufacturers can assess and mitigate the risks associated with potential cross-contamination in shared manufacturing facilities. This guideline provides a framework for determining acceptable levels of residual contamination to ensure the safety and efficacy of medicinal products.
The ICH Q7 Good Manufacturing Practice Guide for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients serves as an internationally recognized standard for GMP compliance in the manufacturing of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Within this guide, specific considerations are provided regarding cleaning validation to ensure the quality, purity, and consistency of APIs. By adhering to the principles outlined in ICH Q7, manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high standards of GMP compliance, including rigorous cleaning validation procedures.
The PIC/S (Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme) Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products offers comprehensive guidance on GMP compliance for pharmaceutical manufacturing. This guide covers various aspects of manufacturing operations, including cleaning validation requirements, to ensure product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance. By following the recommendations outlined in the PIC/S guide, manufacturers can enhance their GMP compliance efforts and uphold the integrity of their manufacturing processes.
Cleaning validation guidelines and protocols, as outlined by regulatory bodies such as the US FDA, are indispensable for ensuring the cleanliness, safety, and compliance of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. By adhering to these guidelines, pharmaceutical companies can effectively validate cleaning procedures, set acceptance criteria, and document protocols to meet cGMP regulations. Critical parameters, sampling plans, MACO calculations, and appropriate analytical methods are essential components of cleaning validation studies.
Furthermore, comprehensive documentation and adherence to regulatory information, including FDA guidance, PDA Technical Reports, EMA guidelines, ICH standards, and PIC/S recommendations, are paramount for maintaining product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance throughout the manufacturing process. Overall, a thorough understanding and implementation of cleaning validation guidelines and protocols is essential for upholding quality standards and ensuring the integrity of pharmaceutical products.