
GAMP 5 (Good Automated Manufacturing Practice) guidelines have been pivotal in establishing industry standards for validating computerized systems in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical devices. With the release of the GAMP 5 Second Edition, significant updates have been aimed at modernizing and refining the approach to Computer System Validation (CSV) and Good Automated Manufacturing Practices (GxP) compliance. The changes incorporate evolving software development practices, emerging technologies, and regulatory shifts, ensuring the framework remains relevant in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven environment.
GAMP 5 Guide, 2nd Edition emphasizes a shift from focusing on compliance to prioritizing patient safety and product quality. This approach aligns with the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) vision, which advocates for a more agile and efficient manufacturing process. The goal is to produce high-quality drug products consistently, with minimal regulatory intervention, moving beyond the baseline requirements of CGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practices).
The second edition encourages the development of robust quality management systems that meet regulatory standards and enhance operational flexibility. This ensures that manufacturers maintain the highest safety and quality standards while being responsive to evolving industry needs. This transition supports CDER’s broader objective of fostering a manufacturing environment that is both compliant and capable of achieving excellence in drug production.
This article highlights the fundamental changes introduced in the GAMP 5 Second Edition. It focuses on integrating Agile methodologies, recognizing new technologies like AI/ML, blockchain, and cloud computing, and emphasizing critical thinking throughout the validation process. These updates ensure the GAMP framework aligns with current industry best practices and regulatory standards.
1. Introduction of Agile Methodologies in Validation
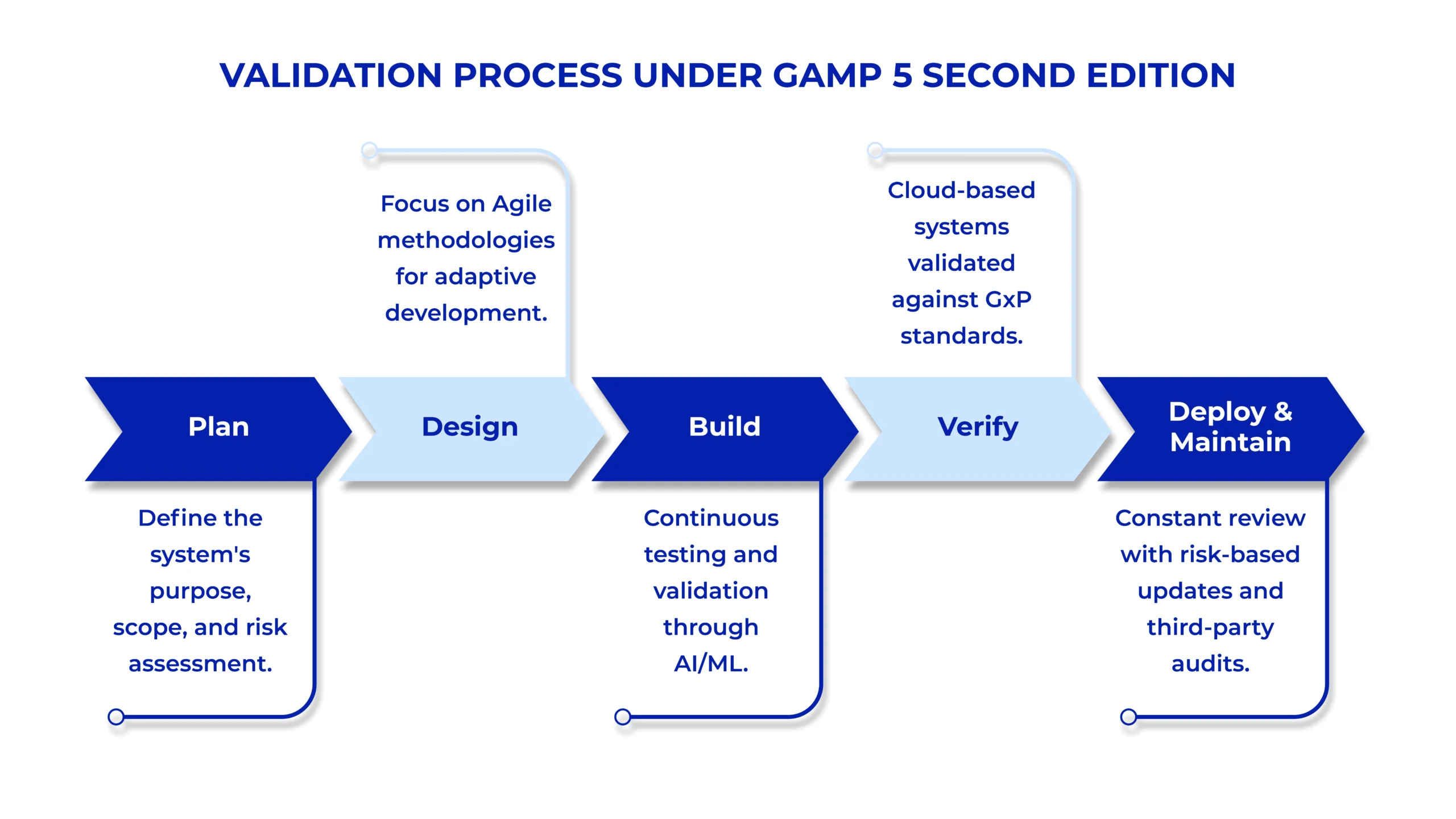
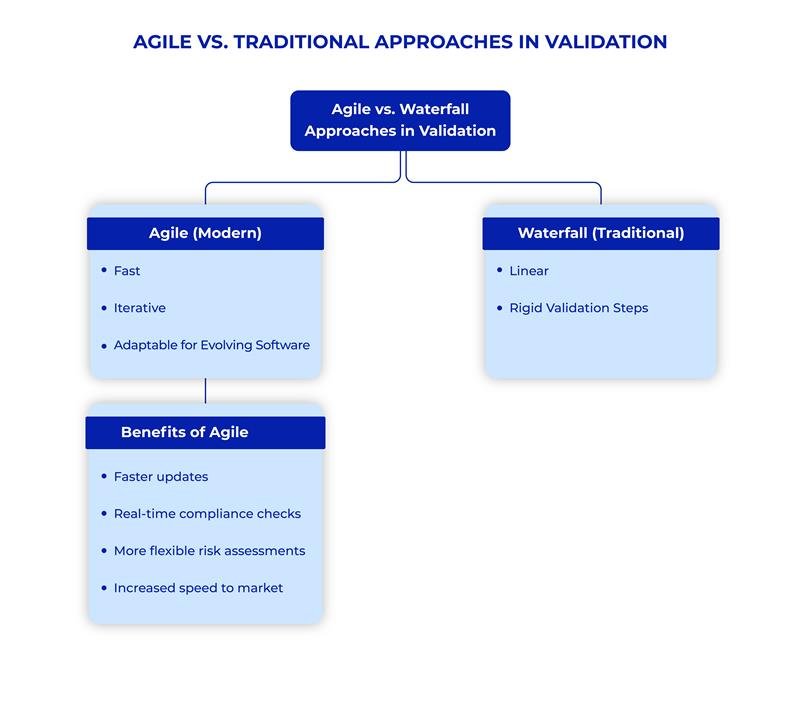
Traditionally, GAMP 5 adhered to a linear development and validation process, heavily reliant on the V-Model. The V-Model, which emphasizes a waterfall approach of sequential steps Analyze, Design, Build, Test, and Deploy was suitable for older, less frequently updated software. However, modern software development, driven by rapid changes and iterative processes, requires more flexibility.
The Second Edition embraces Agile methodologies, which enable a more flexible and iterative approach to software development. This update allows for non-linear development cycles, accommodating the evolving nature of software, particularly in cloud computing and SaaS environments. Agile practices offer incremental validation, enabling faster adjustments and ensuring the system is continually assessed throughout its lifecycle.
This change moves away from the traditional, static approach to validation and embraces an adaptable process suited to dynamic, fast-paced environments.
2. Focus on Emerging Technologies: AI/ML and Blockchain
One of the most notable changes in the GAMP 5 Second Edition is its focus on new technologies. As industries increasingly adopt cutting-edge innovations, GAMP has updated its framework to include guidelines for Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Blockchain.
Appendices have been added or updated to address these emerging technologies. AI and ML technologies, which have begun to play a crucial role in automated manufacturing and regulatory compliance, require specific validation approaches. For instance, the decision-making processes of AI-based systems need rigorous validation to ensure their outputs are accurate, reliable, and compliant with regulatory standards.
Similarly, blockchain and distributed ledger technologies (DLT), which provide robust data integrity and transparency, have been incorporated into the guidelines. A new appendix, M12, covers how these technologies should be integrated into the GAMP framework to maintain data integrity and traceability across distributed systems.

3. Critical Thinking Emphasis
The Second Edition of GAMP 5 introduces a stronger emphasis on critical thinking throughout the validation process. In line with the FDA’s updated Computer Software Assurance (CSA) guidance, critical thinking is no longer considered an optional or secondary consideration.
Critical thinking is now recognized as a core pillar of the GAMP 5 framework, encouraging professionals to assess systems with a patient-centered, risk-based mindset. Rather than rigidly following prescribed procedures, validation teams are encouraged to challenge assumptions and consider broader perspectives, ensuring that each system’s fit-for-use status is thoroughly evaluated.
This updated approach aligns closely with the FDA’s 2022 CSA guidelines, highlighting the need for thoughtful, risk-based decision-making rather than relying solely on documentation. It also underscores the importance of flexibility and the understanding that not every system requires the same level of scrutiny.
4. Incorporation of Risk Management Principles
Risk-based approaches have always been a fundamental part of the GAMP 5 framework, but the Second Edition strengthens this focus. The update further aligns GAMP 5 with the ISO 14971 standard for risk management in medical devices. By emphasizing risk-based thinking, the guidelines now focus on the entire lifecycle of a system, from design to decommissioning, ensuring that risks are continuously evaluated and mitigated throughout.
This updated risk management approach is particularly relevant for modern systems like cloud services, which require ongoing risk assessments due to their dynamic nature. Validation efforts must now focus on the critical aspects of systems that pose the highest risk to product quality, patient safety, and compliance.
5. Updated Guidelines for Cloud Computing
As cloud computing expands across regulated industries, the GAMP 5 Second Edition has incorporated specific guidelines to address the unique challenges cloud-based systems pose.
The guidelines now clearly distinguish between on-premise systems and cloud services, offering practical advice on evaluating the risks associated with cloud vendors, data integrity, and system validation in a cloud environment. With cloud services becoming a critical part of many modern manufacturing operations, GAMP 5 now provides more straightforward frameworks for managing these environments within GxP compliance.
6. Agile and 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance
A significant update in the GAMP 5 Second Edition addresses the intersection of Agile methodologies and 21 CFR Part 11, the FDA regulation that governs electronic records and signatures.
Traditionally, Part 11 required that validation deliverables be approved with formal signatures. However, the Second Edition recognizes that in Agile environments, approval mechanisms can take many forms status changes, email confirmations, or audit trails and don’t necessarily require the traditional handwritten signature approach.
This change reflects a more practical, technology-forward view of what constitutes an approved record.
7. Updated Appendices on Software Tools and IT Infrastructure
The Second Edition provides updated appendices that reflect the growing importance of software tools and IT infrastructure in validating automated systems. The guidelines now explicitly mention using software development tools, cloud-based infrastructure, and open-source software (OSS).
By embracing these technologies, GAMP 5 now offers frameworks to validate the end system and the underlying tools and infrastructure that support its development and operation. These additions help ensure the systems are scalable, reliable, and compliant with GxP regulations.
8. Clarification of Legacy Validation Documents
Another critical change in the Second Edition of GAMP 5 is discontinuing certain legacy validation documents. Traditional documents like Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ), which were commonly used in older validation frameworks, are less relevant to modern development practices.
Instead, the focus has shifted toward continuous validation and agile approaches that allow systems to evolve and be updated more frequently. The Second Edition offers precise guidance on replacing these legacy processes with more flexible, continuous validation activities that reflect current software development trends.
9. Support for Open-Source Software
The growing use of open-source software (OSS) has raised questions about its applicability in regulated industries. The GAMP 5 Second Edition addresses this issue directly by offering guidance on validating OSS in a GxP environment.
This includes evaluating OSS components’ integrity, security, and traceability, which are increasingly integrated into commercial products. The framework provides tools to assess the risks associated with OSS and ensure compliance with the necessary standards.
10. Stronger Focus on IT Providers and Vendor Management
Finally, the Second Edition emphasizes the role of IT providers and vendor management. Ensuring that these providers meet the same compliance standards as in-house teams is crucial with the increasing reliance on third-party vendors for cloud infrastructure, software development, and maintenance.
The Second Edition introduces updated guidelines for assessing and managing the risks associated with external suppliers and service providers. This includes ensuring third-party systems comply with GxP standards and maintain data integrity and security across the lifecycle.
The GAMP 5 Second Edition represents a significant evolution of the original framework, aligning it with modern software development practices, new technologies, and evolving regulatory expectations. By embracing Agile methodologies, focusing on critical thinking, and incorporating the latest technological advancements such as AI/ML, blockchain, and cloud computing, GAMP 5 remains a cornerstone for ensuring GxP compliance and maintaining the integrity of automated manufacturing systems.
These 10 key changes reflect the industry’s changing landscape and offer enhanced flexibility, efficiency, and adaptability for organizations working in regulated environments. As the automation landscape evolves, GAMP 5 remains an essential guideline for Computer System Validation and ensuring systems meet the highest quality, security, and compliance standards.
At AmpleLogic, we recognize that stringent compliance and rigorous validation processes are paramount in today’s dynamic and highly regulated technological landscape. Our advanced GAMP software solutions are engineered to seamlessly integrate with your complex manufacturing ecosystems, enabling the highest levels of operational excellence while ensuring adherence to the highest GxP standards. With our advanced capabilities in optimizing workflows, maintaining unyielding data integrity, and empowering real-time compliance monitoring, AmpleLogic’s industry-leading tools guarantee that your systems remain consistently audit-ready.
We deliver the ultimate efficiency, precision, and regulatory adherence, setting the benchmark for excellence in the industry.





















