
A 21 CFR Part 11 compliant document management system (DMS) is a digital infrastructure designed to meet the FDA’s strict requirements for handling electronic records and electronic signatures. This standard is essential for pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies that submit data to the FDA or maintain electronically regulated records.
The following analysis provides a detailed, data-driven explanation of what these systems are, how they function, and their measurable impact on regulated industries, with reference to current industry trends and regulatory enforcement.
The Legal and Regulatory Foundation
21 CFR Part 11, introduced by the FDA in 1997, is a federal regulation that defines the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered credible and equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures. This rule applies to all FDA-regulated organizations that create, modify, maintain, archive, retrieve, or transmit records in electronic form.
The regulation was developed in response to the increasing use of computerized systems in research, manufacturing, and quality management, as well as the need to address risks associated with data manipulation, unauthorized access, and record loss.
Core Requirements of a 21 CFR Part 11 Compliant Document Management System
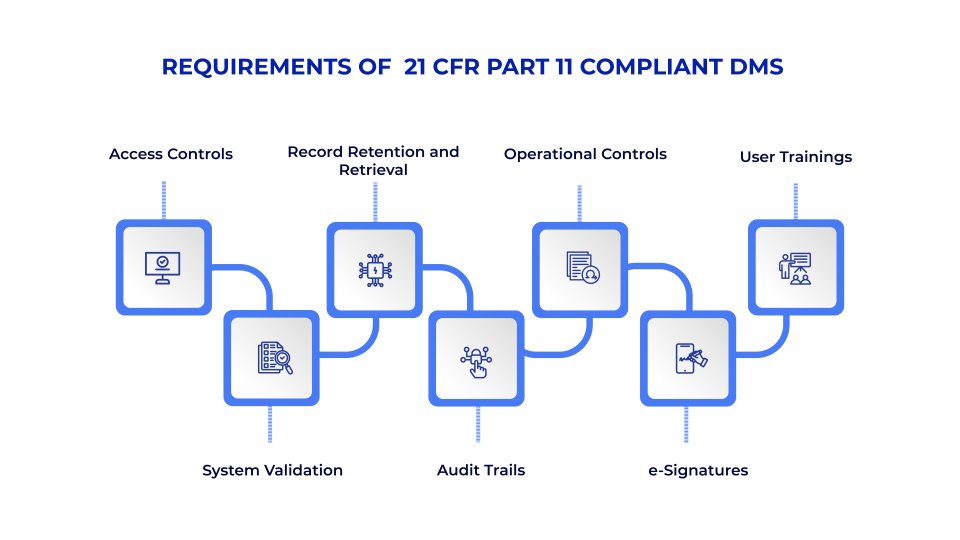
A compliant DMS must address several technical and procedural requirements:
1. System Validation
Validation is the documented process of proving that a system does what it is intended to do, consistently and reliably. FDA inspectors frequently request validation evidence during audits.
For example, in 2024, 28% of FDA warning letters related to electronic records cited inadequate validation.
2. Audit Trails
Every action involving a regulated document creation, modification, or deletion must be automatically logged. Audit trails must capture the user, timestamp, and nature of the action, and these logs must be tamper-evident and retained for as long as the record itself.
E.g., According to a 2023 survey of life sciences companies, 91% reported using audit trails to support regulatory inspections.
3. Electronic Signatures
Electronic signatures must be unique to each user, securely linked to the record, and include the signer’s name, date, time, and purpose. The system must prevent unauthorized use or reassignment of signatures. Two-factor authentication is standard. The FDA requires that electronic signatures be at least as secure as handwritten signatures.
4. Access Controls
Only authorized users should be able to view or modify records. Permissions are typically role-based, and passwords must be regularly updated. In 2024, 37% of FDA data integrity findings involved inadequate access controls.
5. Record Retention and Retrieval
Records must be stored securely and be readily accessible for the entire retention period required by regulation. Companies must be able to produce records promptly during FDA audits. Automated archiving, backup, and disaster recovery are standard features.
6. Operational Controls
The system must enforce proper sequencing of tasks and restrict actions to authorized personnel. Device checks and authority checks are required to maintain control over data input and system use.
7. User Trainings
All users must be trained in both the system and regulatory requirements. Training records are often managed within the DMS itself.
Document Management System Functions
A 21 CFR Part 11 compliant DMS automates the creation, review, approval, distribution, and archiving of documents. Important features include:
- Automated workflows for document routing and approval
- Secure electronic signature capture
- Version control to ensure only the latest approved documents are in use
- Instant retrieval of records for audits or inspections
- Role-based access and permissions
- Regular system backups and disaster recovery
- Easily manage document prints using DMS Software.
Cloud-based DMS solutions have become increasingly common, offering secure access from multiple locations and reducing the burden of IT maintenance. In 2024, 57% of new DMS implementations in the life sciences sector were cloud-based.
Industry Data and Trends
- Analysis of 15 years of FDA warning letters (2010–2020) showed that 21% of all violations were related to documentation and data integrity.
- Companies using 21 CFR Part 11 compliant DMS platforms reported a 35% reduction in document processing time and a 23% decrease in audit preparation costs, according to a 2023 benchmark report.
- 41% of reported healthcare data breaches in 2024 were related to hacking or IT incidents, highlighting the importance of robust electronic controls.
- In a 2023 survey, 38% of life sciences companies reported that FDA inspections now routinely include a review of electronic systems and audit trails.
Implementation and Cost
The cost of a compliant DMS depends on the number of users, modules, and support required. Subscription models are typical, with pricing that includes hosting, validation, training, and support. Implementation for a mid-sized company usually takes between two and four months, with validation and user training as critical milestones. Total cost of ownership includes not just software licensing but also validation, staff training, ongoing support, and periodic re-validation after system updates. Companies often allocate 10-15% of their quality or IT budgets to maintain compliance with 21 CFR Part 11.
Regulatory and Business Impact
Non-compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 can result in warning letters, product recalls, or criminal penalties. In 2024, FDA data shows that inadequate document controls and audit trails were among the top reasons for enforcement actions. For companies operating globally, a compliant DMS also supports compliance with other regulations, such as EU Annex 11 and ISO 13485.
A compliant DMS not only reduces regulatory risk but also improves operational efficiency, data integrity, and audit readiness. Companies that invest in robust systems are better positioned to respond to regulatory changes, scale their operations, and maintain trust with regulators, partners, and patients.
Selecting a 21 CFR Part 11 Compliant DMS
When evaluating DMS options, organizations should consider:
- System validation documentation and ongoing support for maintaining a validated status.
- Security features such as strong encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
- Integration capabilities with other quality management systems, such as CAPA, LMS, and change control modules.
- Scalability to accommodate growth in users, records, and regulatory requirements.
- Vendor reputation and a proven track record in the life sciences sector.
Conclusion
A 21 CFR Part 11 compliant document management system is a necessity for FDA-regulated organizations that manage electronic records. It provides the controls and traceability needed to meet regulatory requirements, supports efficient business operations, and reduces the risk of non-compliance. As regulatory scrutiny increases and digital recordkeeping becomes the norm, investing in a compliant DMS is essential for maintaining data integrity and operational reliability.





















