The pharmaceutical industry, a critical healthcare innovation and delivery sector, relies heavily on digital transformation for research, patient care, and business operations. This rapid digitization comes with increasing challenges in safeguarding sensitive data. From intellectual property to patient records, the data held by pharmaceutical companies is highly sought after by cybercriminals, making robust data privacy and security measures indispensable.
Understanding the Types of Data Handled in Pharma
Pharma organizations manage various categories of data that demand stringent protection due to their sensitivity and value:
a. Patient Data
Patient data includes medical histories, diagnoses, treatments, and genomic data. For instance, electronic health records (EHRs) digitally store all pertinent patient information, enabling efficient healthcare delivery. However, any breach of this data can lead to identity theft, discrimination, or misuse of unauthorized research. With personalized medicine gaining traction, genomic data is increasingly used, necessitating even stricter security due to its direct link to individual identities.
b. Clinical Trial Data
Clinical trials generate extensive datasets, from patient enrollment information to test results and methodologies. Unauthorized access to this data can jeopardize trial outcomes, compromise patient safety, and damage a company’s reputation. Cyberattacks targeting trial data can delay drug approvals, leading to significant financial and public health repercussions.
c. Intellectual Property (IP)
Pharmaceutical innovations, including drug formulations, research methodologies, and patented technologies, form the backbone of a company’s competitive edge. If this data is leaked or stolen, it can result in counterfeit drugs entering the market or competitors gaining undue advantage.
d. Operational Data
This encompasses information on supply chain logistics, production schedules, vendor contracts, and employee details. A breach here can disrupt manufacturing pipelines, delay deliveries, and expose sensitive internal operations.
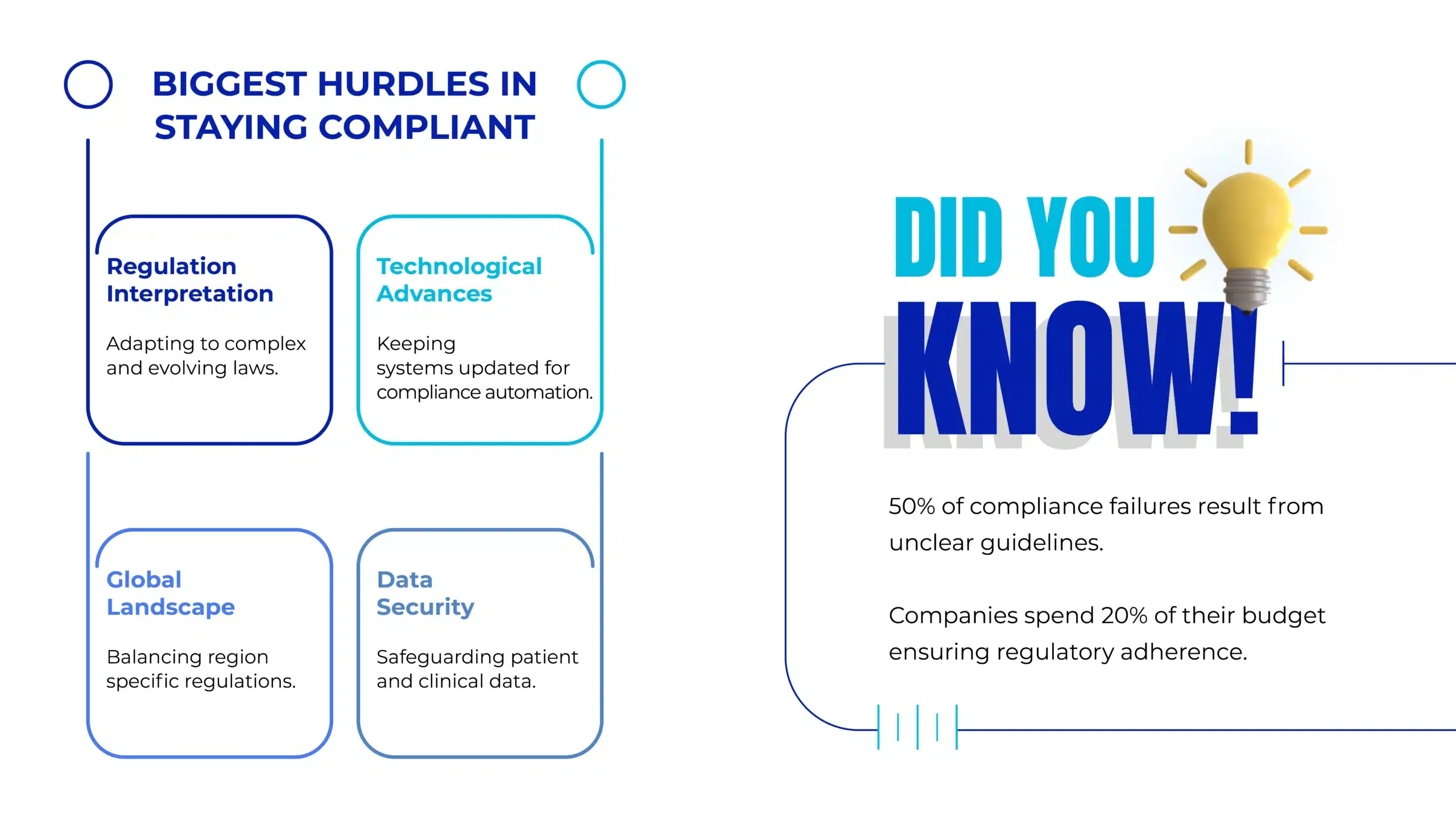
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Pharma Data Privacy
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide enforce strict laws to protect data in the pharmaceutical sector. These regulations guide how data should be collected, stored, processed, and shared, imposing penalties for non-compliance. Let’s explore the most critical frameworks:
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA governs the handling of Protected Health Information (PHI) in the U.S. It mandates that organizations implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure PHI’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Security Rule: Organizations must implement encryption, authentication, and access control to protect electronic PHI.
Breach Notification Rule: In case of a breach, organizations must notify affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and sometimes the media, ensuring transparency and accountability.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR, applicable across the EU, sets a global standard for data protection. It emphasizes:
Data Minimization: Organizations should collect only the data that is strictly necessary.
Explicit Consent: Patients must provide clear and informed consent for their data to be used, ensuring transparency and control over personal information.
Right to Erasure: The “right to be forgotten” allows individuals to request the deletion of their personal data under specific circumstances.
FDA’s Data Integrity Guidelines
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration enforces stringent data integrity standards for pharmaceutical companies. Adhering to ALCOA+ principles ensures data is:
Attributable: Every action or modification must be traceable to its source.
Contemporaneous: Data should be recorded during the event, eliminating the scope for falsification.
India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act)
India’s emerging data privacy law introduces key mandates like data localization, requiring sensitive data to be stored within Indian borders, and explicit accountability measures for demonstrating compliance.
Challenges in Pharma Data Privacy and Security
1. Complex Data Ecosystems
Pharmaceutical companies manage vast datasets across multiple systems, challenging comprehensive security oversight.
2. Global Collaboration
Cross-border research partnerships necessitate compliance with diverse privacy regulations, often creating operational complexities.
3. Technological Adoption
Emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing bring innovation but also introduce new vulnerabilities.
4. Insider Threats
Employees with access to sensitive data may unintentionally or maliciously compromise security, underscoring the need for stringent monitoring.
The Consequences of Lapses in Data Security
Failing to secure data can have catastrophic consequences:
- Financial Losses: Intellectual property theft and operational disruptions can cost billions.
- Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with HIPAA or GDPR can result in hefty fines.
Reputation Damage: Breaches erode public trust, impacting patient relationships and market positioning.
Latest Cybersecurity Incidents in Pharma
1. Sun Pharmaceuticals Ransomware Attack
In 2023, Sun Pharmaceuticals fell victim to the ALPHV ransomware group, causing significant operational disruptions and data exposure.
2. AIIMS Cyberattack
India’s premier medical institution, AIIMS, faced a data breach in 2023, exposing sensitive patient information and halting operations for days.
3. Global Findings
According to the Indusface Annual State of Application Security Report 2023:
Over 5 billion cyberattacks targeted Indian enterprises, with healthcare being a prominent sector.
The most common vulnerabilities included:
Malicious Content: Software integrity failures.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Allowing unauthorized data manipulation.
Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF): Exploiting server vulnerabilities.
Technologies Enabling Data Privacy and Security
Encryption
Encryption transforms data into unreadable formats unless decrypted using authorized keys.
-
AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard): Widely regarded as the gold standard for encrypting data at rest.
-
TLS (Transport Layer Security): Encrypts data in transit, such as during communication between pharmaceutical systems and external entities.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
ZTA assumes that no entity, internal or external, is inherently trustworthy. Instead, every access request is verified continuously.
-
Micro-Segmentation: Divides the network into smaller zones, limiting access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel.
-
Adaptive Authentication: Factors like user behavior, location, and device type determine access, mitigating risks of compromised credentials.
Blockchain in Clinical Trials
Blockchain technology creates a tamper-proof ledger for recording trial data, improving transparency and trust. For example:
-
Participants’ consent can be recorded securely, ensuring compliance with ethical standards.
-
Researchers can track every data modification, preserving integrity and avoiding manipulation.
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Artificial Intelligence helps detect anomalies in network behavior, signaling potential cyber threats. For instance:
-
AI systems can identify unusual login patterns, such as access from unrecognized devices or unexpected geographical locations.
-
Real-time threat intelligence can trigger automated responses, like isolating affected systems.
Best Practices for Pharma Data Protection
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
This ensures employees access only the data necessary for their role. For instance, a manufacturing technician might access production data but not intellectual property documents.
Regular Penetration Testing
Simulating cyberattacks helps identify and rectify vulnerabilities before actual attackers exploit them.
Incident Response Playbooks
Having pre-defined protocols for responding to breaches minimizes downtime and limits data exposure. These playbooks should include steps for containment, investigation, and recovery.
Key Security Practices
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit prevents unauthorized access during breaches.
- Access Controls: Implementing role-based access, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regular audits limits data exposure.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Ensuring vendors comply with established security standards mitigates external risks.
- Data Minimization: Collecting and retaining only essential data reduces exposure to breaches.
- Employee Training: Continuous education on recognizing threats, handling data, and responding to incidents enhances organizational security.
Strategies to Strengthen Data Security in Pharma
Robust Data Governance Framework
Clear ownership, access protocols, and retention policies ensure structured data management.
2. Advanced Cybersecurity Measures
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Actively monitoring for malicious activity.
- Regular Penetration Testing: Identifying system vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Incident Response Plans: Quick and effective responses to minimize breach impacts.
3. Privacy by Design
Incorporating security measures during the development phase of digital systems ensures inherent protection.
4. Data Pseudonymization
Removing identifiable information while retaining research value reduces risks during collaborations.
5. Zero-Trust Security Models
Treating all network access as a potential threat and verifying every request prevents unauthorized data handling.
Comprehensive Security Across AmpleLogic’s Software Solutions
AmpleLogic ensures that all its software solutions are equipped with advanced security measures, enabling organizations to operate securely while complying with global standards. Our products, including Quality Management Systems (QMS) and Electronic Batch Manufacturing Records (eBMR), integrate state-of-the-art technologies to guarantee data integrity, robust access control, and operational scalability. Each system is fortified with real-time monitoring, encryption, and automated processes, safeguarding sensitive information against unauthorized access and cyber threats, all while streamlining workflows across the organization.
AmpleLogic’s User Access Management (UAM) Software is a cornerstone of our secure ecosystem, explicitly designed for highly regulated industries like pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. This platform eliminates the inefficiencies of manual user access processes by providing Seamless Integration, Automated Lifecycle Management, Enhanced Compliance, and Optimized Resource Utilization. By leveraging this system, businesses can mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access, duplicate identities, and expired permissions. The role-based permissions ensure access is fully aligned with organizational policies, while the audit-ready design facilitates seamless inspections.
Furthermore, AmpleLogic’s suite of products, such as the Regulatory Information Management System (RIMS), Stability Management System, and Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS), are tailored to manage sensitive data across clinical trials, operational processes, and regulatory compliance. These solutions provide end-to-end visibility and control, ensuring that data integrity and compliance are maintained throughout every process stage, from development to manufacturing.
Discover how AmpleLogic’s advanced software solutions can strengthen your data security and ensure compliance with industry regulations. With inherent features across our portfolio, we deliver secure, scalable, and compliant operations tailored to the unique needs of life sciences and beyond. Contact us to learn more.