Glossary
MACO (Maximum Allowable Carryover)
What is MACO?
The Maximum Allowable Carryover (MACO) calculation is a critical, science-driven component of pharmaceutical cleaning validation that makes sure of both patient safety and manufacturing compliance. The proper derivation and application of MACO values underpin cleaning acceptance criteria, influence sampling limits, and support effective control of cross-contamination in multi-product manufacturing environments.
With evolving regulatory expectations, the accuracy and defensibility of MACO calculations have become important to securing uninterrupted product supply and avoiding costly recalls and enforcement actions.
Regulatory Scrutiny on Cleaning Validation
Inspection reports from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and India’s Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) highlight increasing oversight of cleaning validation practices.
Between 2022 and 2024, the FDA recorded a 27% rise in Form 483 observations related to cleaning validation, with over half due to incomplete or unjustified Maximum Allowable Carryover (MACO) calculations. Notably, 18% of cited firms defaulted to fixed 10 ppm residue limits without toxicological risk assessments or scientifically justified alternatives.
What is MACO Value: Definition and Role in Cleaning Validation
Maximum Allowable Carryover (MACO) is the calculated threshold for the amount of residue from a previously manufactured product that can remain on shared manufacturing equipment before producing the next batch, without posing risk to patient safety or product quality. In multiproduct environments, MACO forms the technical and regulatory backbone of any cleaning validation program.
Characteristics of MACO Value
- Not a fixed industry value – MACO must be product- and process-specific.
Derived from:
- Toxicological data
- Dosage information
- Legacy default values (where permitted, but with lower regulatory acceptance)
Limits vary widely:
- Potent oncology API: often in the low microgram range
- Inert nutraceutical excipient: higher permissible limits
- The determining factor: potential patient harm from cross-contamination.
Operational Integration
MACO directly influences:
- Setting acceptance criteria for cleaning validation swab and rinse tests.
- Designing and optimizing cleaning procedures that are effective without excessive resource use.
- Preparing defensible documentation for inspections by CDSCO, FDA, EMA, and other regulators.
Risks of Misapplication
- Compliance risk from defaulting to unsubstantiated fixed limits (e.g., 10 ppm) or applying one-size-fits-all safety factors.
- Operational inefficiency:
- Overly strict limits → unnecessary re-cleans, wasted resources.
- Overly lenient limits → risk of audit failures or contaminated batch release.
Regulatory Expectations
Agencies expect a traceable, scientifically defensible chain from product data to MACO value, including:
- Laboratory toxicology reports
- Pharmacological dose data
- Batch size information
- Validated analytical methods
- Clear integration into cleaning SOPs
Every link in this chain must be technically sound and well-documented to withstand inspection.
MACO Calculation Methods
Determining an accurate, defensible MACO value is not a one‑size‑fits‑all exercise. Regulatory authorities globally recognize three main calculation approaches, each with a different scientific basis, regulatory standing, and level of patient safety control.
Understanding these methods in detail not only confirms compliant cleaning validation but also helps in selecting the most appropriate, risk‑proportionate limit for each product changeover.
1. Legacy 10 ppm Method
The 10 ppm method is the oldest and simplest way to derive MACO. It fixes the allowable residue level at 0.001% (10 parts per million) of the smallest batch size of the next product. It emerged in an era when toxicological data were often incomplete or unavailable, and served as a conservative rule‑of‑thumb to prevent gross contamination.
Today, many regulators view it as a legacy approach suited only for non‑potent products or as a “sanity check” when more sophisticated calculations produce higher limits than this default.
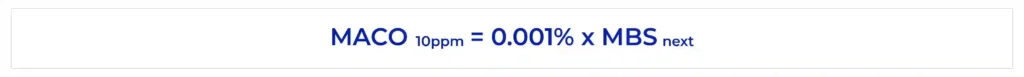
Example 1:
- Next product batch = 300 kg = 300,000 g = 300,000,000 mg
- MACO = 0.00001 × 300,000,000 = 3,000 mg (3 g)
Example 2:
- Next batch = 150 kg = 150,000 g = 150,000,000 mg
- MACO = 0.00001 × 150,000,000 = 1,500 mg (1.5 g)
Regulatory observations:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Very simple to implement | Ignores product potency, toxicity, and therapeutic dose |
| Requires only one data point (batch size) | Can be either over-restrictive or under-protective |
| Provides a common reference point for benchmarking | Regarded as scientifically weak except for comparison purposes |
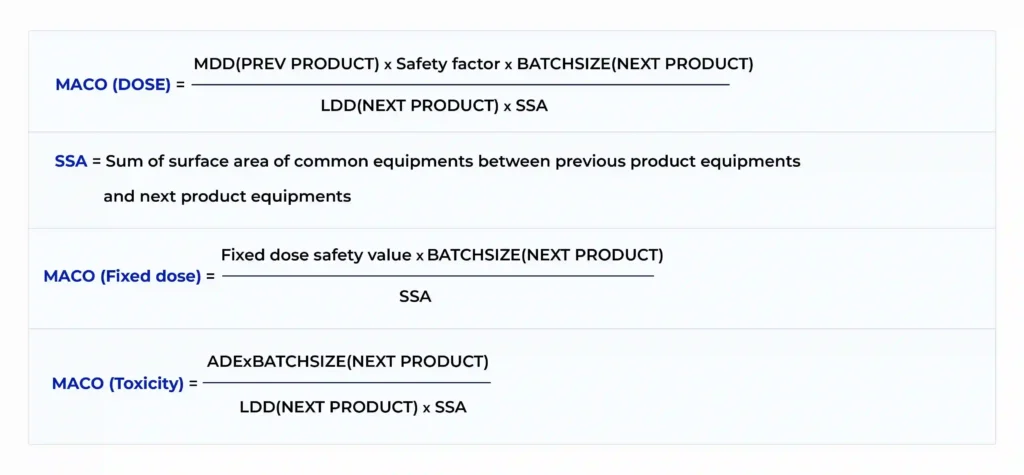
2. Dose‑Based Method with Safety Factor in MACO Calculation
This method incorporates pharmacological information, specifically the minimum therapeutic dose (MTD) of the previous product and the maximum daily dose (MDD) of the next, plus a safety factor in MACO calculation to account for patient variability, toxicological uncertainty, and analytical detection limits. The safety factor is critical and must be chosen deliberately, based on route of administration, vulnerability of the target population, and product class.
Formula:

Example 1:
- MTD_prev = 10 mg
- MBS_next = 500,000,000 mg
- SF = 1,000
- MDD_next = 1,000 mg
- MACO = (10 × 500,000,000) ÷ (1,000 × 1,000) = 5,000 mg = 5 g
Example 2:
- MTD_prev = 5 mg
- MBS_next = 200,000,000 mg
- SF = 10,000 (injectable)
- MDD_next = 500 mg
MACO = (5 × 200,000,000) ÷ (10,000 × 500) = 200 mg
Regulatory observations:
- EMA’s 2023–2024 inspection data shows 31% of dose‑based MACOs fail compliance due to inappropriate or generic SF selection.
- FDA expects justification for each SF, citing literature, toxicity data, or internal risk studies.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Considers product-specific dosing information | Relies on accurate MTD/MDD data |
| Safety factor allows built-in precaution | SF can be prone to arbitrary assignment if not justified |
3. MACO Calculation Using PDE (Health‑Based Approach)
This is the preferred modern standard. It uses the Permitted Daily Exposure (PDE), a toxicology‑derived safe intake value for humans that incorporates the No Observed Effect Level (NOEL), body weight, and uncertainty factors to account for data quality, variability, and extrapolation from animal studies.
By grounding MACO in PDE, this approach ensures that exposure from residue never exceeds a scientifically established safe daily limit for any patient.
Formula:

Example 1:
- PDE_prev = 0.5 mg/day
- MBS_next = 500,000,000 mg
- MDD_next = 1,000 mg
MACO = (0.5 × 500,000,000) ÷ 1,000 = 250,000 mg (250 g)
Example 2:
- PDE_prev = 0.05 mg/day (highly potent API)
- MBS_next = 200,000,000 mg
- MDD_next = 500 mg
MACO = (0.05 × 200,000,000) ÷ 500 = 20,000 mg (20 g)
Regulatory observations:
- EMA Annex 15 (2023) mandates PDE use for potent APIs.
- 64% of PDE‑related citations in EMA inspections arose from missing, expired, or incomplete toxicology reports.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Directly links limit to toxicological safety | Requires robust toxicological data and interpretation |
| Considered the gold standard by the FDA, EMA, and ICH | More resource-intensive to establish initially |
Comparative Overview: Risk Control Precision
| Method | Data Required | Regulatory Standing | Typical Use Case | Risk Control Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 ppm | Batch size only | Legacy fallback only | Inert, low‑risk products | Low |
| Dose + SF | MTD, MDD, SF, batch | Accepted if SF justified | Medium‑potency oral/ injectable | Moderate |
| PDE‑based | PDE, MDD, batch | Preferred globally | Potent, toxic, high‑risk products | High |
Cleaning Validation Swab Limit Calculation
Once a MACO value is established using one of the recognised methods, whether that is the legacy 10 ppm, the dose‑based formula with safety factor in MACO calculation, or the preferred MACO calculation using PDE, the next step is to translate that number into a residue acceptance limit that can actually be measured in the cleaning validation process. This is where the cleaning validation swab limit calculation comes in.
The swab limit defines the maximum amount of residue permissible on the area sampled by the swab. It links the theoretical MACO value to a tangible pass/fail criterion during equipment sampling.
Swab limit formula:

Example 1 – Using Dose‑Based MACO
MACO = 5,000 mg
Total Equipment Surface Area = 20,000 cm²
Swab Area = 25 cm²
- Calculation:
5,000 ÷ 20,000 = 0.25 mg/cm²
0.25 × 25 = 6.25 mg/swab
Example 2 – Using PDE‑Based MACO
MACO = 250,000 mg
Total Equipment Surface Area = 20,000 cm²
Swab Area = 25 cm²
- Calculation:
250,000 ÷ 20,000 = 12.5 mg/cm²
12.5 × 25 = 312.5 mg/swab
Adjusting for Recovery Efficiency
In reality, swab sampling methods rarely recover 100% of the residue from a surface. If swab recovery is less than 100%, the limit must be corrected so that the measured value corresponds to the theoretical MACO.
Adjusted swab limit formula:

Example Adjusted Limit – Dose‑Based MACO
Swab Limit = 6.25 mg/swab
Recovery = 75%
– Adjusted Limit = 6.25 × (100 ÷ 75) = 8.33 mg/swab
Regulatory expectations:
- Total surface area must be from verified equipment measurements or drawings, not estimates.
- Swab area must be consistent across all tests and match validation documents.
- Swab method recovery should be ≥ 70% unless there is documented scientific justification for a lower value.
- The link from MACO → surface area → swab area → adjusted swab limit must be traceable in documentation.
How AmpleLogic handles this step:
The AmpleLogic Cleaning Validation Management System streamlines this entire process by:
- Storing validated total surface areas for every equipment asset.
- System automatically considers the lowest MACO value out of all the three criteria in order to follow the worst-case approach during execution.
- Auto protocol drafting and execution, where the worst-case product approach based on MACO calculation is followed.
- Generating an audit‑ready report showing calculation steps, parameters used, and authorisation trail, fully aligned with MACO calculation, FDA, and CDSCO expectations.
This removes manual calculation errors, ensures consistency across validation runs, and provides immediate traceability during regulatory inspections.
Calculation by AmpleLogic’s system
Analytical Methods for MACO Verification in Cleaning Validation
Calculating an accurate MACO is only the first step. Proving that your cleaning process consistently meets that limit relies on reliable, validated analytical methods. Regulators expect every cleaning validation protocol to include both clear sampling strategies and proven analytical approaches, with full documentation of method performance.
1. Swab Sampling: The Industry Standard
- Swabbing is the most widely used technique for measuring product residue on equipment surfaces.
- Swab sites are chosen based on risk, typically the “worst-case” locations: hard-to-clean corners, valves, seals, or areas observed in visual inspections to accumulate more residue.
- Standard swab area is usually 25 cm², but always verify with real measurements and document any deviations.
- Swab materials (e.g., polyester, cotton) and solvents must be evaluated for their ability to extract the compounds of interest from the target surfaces.
Validation for Swab Sampling:
- Recovery studies are mandatory. At least three replicate tests, on the same equipment surface materials (stainless steel, glass, PTFE, etc.) as used in production, must confirm ≥70% recovery or provide a documented scientific basis for lower percentages.
- Make sure nothing in the swab or solvents interferes with the analyte measurement.
- Validate that different operators, lots, and environmental conditions don’t cause variation in recovery or detection.
2. Rinse Sampling: When and Why
- Rinse sampling is often used for Clean-in-Place (CIP) systems, internal pipework, or wherever swabbing is impractical.
- Measured by adding a defined volume of solvent (water or process-specific liquid), rinsing the equipment or system, and analyzing the rinse for residual actives.
- Rinse validation ensures the solution volume and procedure are effective for residue collection.
Validation for Rinse Sampling:
- Like swabs, recovery studies must show the extraction efficiency across representative surfaces and process conditions.
- Always use the same amount as validated, not just a convenient amount; differences can lead to misleading results.
3. Analytical Technique Selection
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC):
The gold standard for most drug substances, offering low detection limits and excellent specificity. Essential for potent actives and whenever PDE-based MACOs are calculated to very low levels.- Validation parameters to record: linearity, accuracy, precision, specificity, detection limit, and quantitation limit.
- Validation parameters to record: linearity, accuracy, precision, specificity, detection limit, and quantitation limit.
- Total Organic Carbon (TOC):
Used as a fast, non-specific screening method; ideal for compounds with no chromophore or when a mixture of residues (active + excipients) is present.- TOC is only acceptable when a validated correlation exists between the specific compound (API, cleaning agent) and the TOC signal.
- Method validation must ensure the instrument’s sensitivity matches the MACO-derived acceptance criterion.
- UV/Vis, Conductivity, or Other Methods:
Sometimes preferred for cleaning agents, salts, or excipients. Method must be proven selective for the analyte and not susceptible to interference from process residuals or excipient carryover.
4. Integration and Documentation
- Every analytical method, whether swab, rinse, or instrumental, must be tied back to the residue acceptance limit derived from the MACO calculation and surface/swab/rinse conversion.
- Validation summary reports should be readily available for each cleaning validation, showing method performance data, matrix interference evaluation, working range, and limit of quantification.
- Batch records and cleaning validation summaries must document which validated method was used for each sampling event, and link sample data/results back to method validation records.
- Inspector Expectations
- Regulators usually request to see not only a copy of the method SOP, but also all associated recovery studies, selection logic for sampling sites and methods, and a retesting strategy if initial recoveries fall short.
- Firms succeed at audit time when they demonstrate that sampling and analytic approaches are scientifically planned, realistically validated, and truly relevant to the products and equipment in use.
Auditors know the difference between check-the-box validation and real-world, risk-based method selection. They look for technical understanding, not just protocols, but performance.
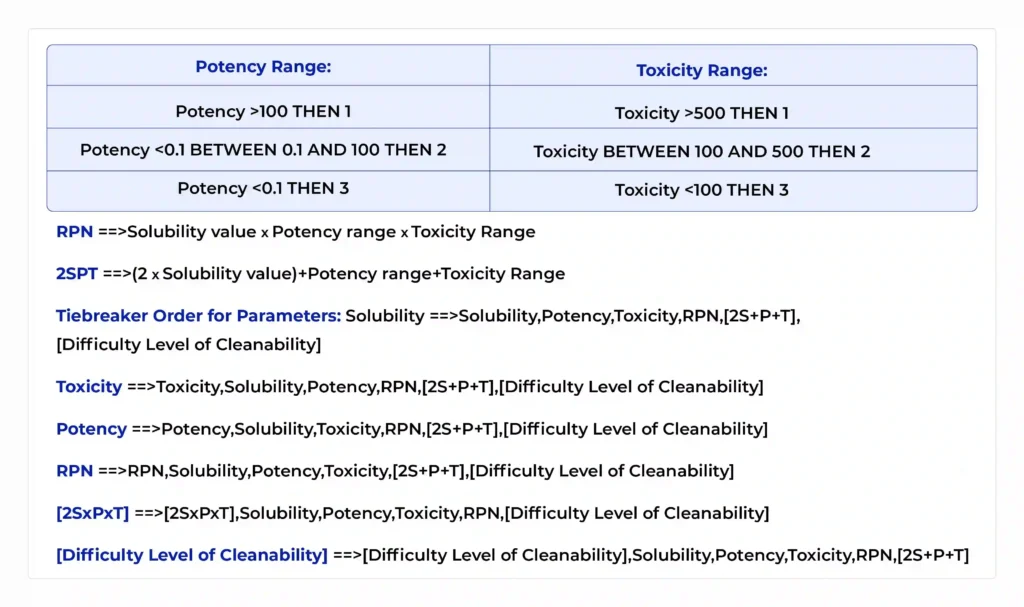
Risk-Based Approaches in MACO Calculation and Cleaning Validation
The pharmaceutical industry increasingly embraces a risk-based mindset to allocate resources efficiently while safeguarding patient safety. MACO calculation and cleaning validation are no exceptions; tailoring limits and sampling strategies according to risk is both a regulatory expectation and operational best practice. The risk factors affecting MACO and Cleaning Validation are –
- Product Potency and Toxicity: Highly potent or cytotoxic APIs require very low MACO limits, stringent sampling, and comprehensive toxicological data integration (preferably via PDE methods). Conversely, non-potent products may tolerate higher carryover thresholds.
- Dosage Form: Injectable and inhalation products typically demand stricter limits and represent higher patient risk than oral solids or topical formulations. This affects safety factors and sampling intensity.
- Batch Size of Next Product: Smaller batches mean the allowed residue dose represents a larger percentage of the next batch; this often tightens MACO limits.
- Equipment Design and Surface Complexity: Complex equipment with small dead legs, seals, and valves challenges cleaning effectiveness and sampling representativeness. Higher risk areas warrant more conservative limits and focused sampling.
- Patient Population: Products intended for immunocompromised, pediatric, or vulnerable populations often require additional safety margins in MACO and cleaning validation acceptance criteria.
Developing a Risk Matrix for MACO
A simple industry‑proven approach is to use a risk matrix that scores each factor (e.g., potency, dose form, batch size, equipment complexity) on scales such as low, medium, and high, with corresponding weighting. This matrix guides:
- Whether to apply a PDE, dose-based, or legacy 10 ppm MACO method.
- The magnitude of the safety factor in dose-based methods.
- The number and location of swab or rinse samples
- Frequency and rigor of re-validation.
Example Risk Matrix
| Risk Factor | Low | Medium | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potency (PDE) | >10 mg/day | 1–10 mg/day | <1 mg/day |
| Dose Form | Oral solids | Topicals | Injectables/Inhaled |
| Batch Size (MBS) | >1000 kg | 100–1000 kg | <100 kg |
| Equipment Design | Simple | Moderate | Complex |
| Patient Group | Adult, healthy | Geriatric | Immunocompromised |
Applying cumulative risk scores directs the MACO calculation method and sampling rigor accordingly; higher risk profiles default to PDE plus conservative safety factors and more intensive sampling.
Advantages of a Risk-Based Approach
- Regulatory Alignment: Aligns with ICH Q9 and WHO risk frameworks, increasing inspection confidence.
- Efficient Resource Use: Focuses effort on product changes and equipment most likely to cause harm, reducing validation burdens for low-risk scenarios.
- Continuous Monitoring: Enables dynamic adjustment of MACO limits and cleaning protocols as product portfolio or equipment usage evolves.
Practical Tips for Implementation
- Involve cross-functional teams, including toxicologists, quality, manufacturing, and process engineers, to develop and validate the risk matrix.
- Regularly review risk scores with new toxicology data, process changes, or inspection feedback.
- Document the rationale behind scoring and decisions thoroughly.
- Use data analytics to identify trends in cleaning failures or rejections and re-align risk priorities as needed.
This risk-based strategy forms the foundation for a scientifically justified, efficient MACO calculation and cleaning validation program that meets today’s tough regulatory expectations without excess cost or delay.
Conclusion
Accurate, scientifically grounded MACO calculation is fundamental to effective cleaning validation and regulatory compliance. As regulatory expectations tighten and technologies evolve, automation platforms like AmpleLogic offer unparalleled advantages by streamlining calculations, ensuring audit-ready documentation, and embedding risk-based principles directly into manufacturing workflows.
To safeguard patient safety, reduce audit risks, and optimize cleaning efficiency, pharmaceutical manufacturers should consider implementing AmpleLogic’s comprehensive cleaning validation management solution, transforming MACO calculation from a compliance challenge into a competitive advantage.

















