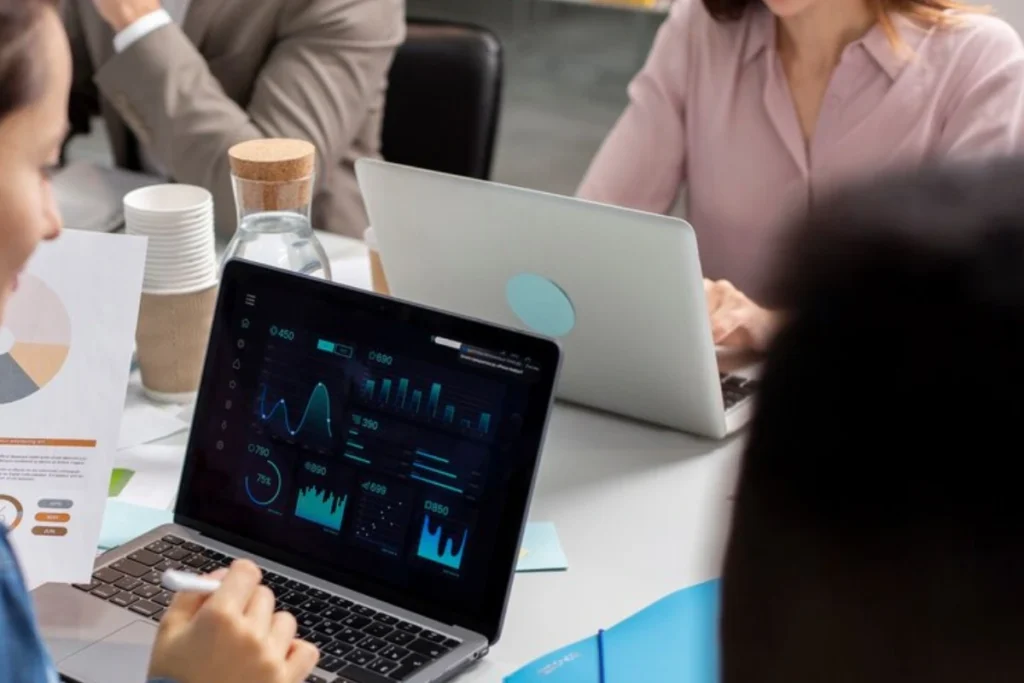
QC heads often face trouble while planning and tracking Quality Control tests in their labs. They have to plan numerous tests every day to ensure consistent product quality, safety and regulatory compliance. Supervisors generally keep track of large sets of data of quality control analysts, equipment, test batches, test processes, instruments, shift timings, regulations and so on. To further understand the intricacies of Quality Control tests, lets first understand why Quality Control tests are conducted in pharma.
Later, we will discuss the types of quality control tests that are conducted, the challenges in QC Planning and Scheduling, the best practices that can be implemented to address these challenges and finally propose a solution that can effectively streamline and bring accuracy in QC planning and scheduling.
What is Quality Control in Pharma?
Quality Control (QC) involves examination and testing of pharmaceutical products at different stages of the production. It helps identify defects in product quality and rectifies these errors to maintain consistent product quality. QC tests help mitigate the risk of product recalls, legal repercussions that might affect an organization’s reputation, reliability and integrity.
Types of Quality Control Tests
Raw Material Testing
This involves evaluation of raw materials for production of quality pharma products. Identity Testing, Purity Testing, Assay Testing, Microbial Testing are some underlying tests that ensure that raw materials are free from contamination.
In-Process Testing
Measures the quality of intermediate products at various stages of the manufacturing process. This includes monitoring critical process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and pH to ensure they remain within specified ranges and periodically test pharma products to detect deviations or issues early in the process.
Final Product Testing
Conducted on finished products to verify if they meet all quality attributes and regulatory requirements before being released for distribution. Assay, Dissolution Testing, Stability Testing and Packaging Integrity Testing are the common tests that take place in final product testing.
Physical-Chemical Laboratory Tests
The Physical-Chemical Laboratory tests the physical and chemical properties of pharmaceutical products, including measures tablet hardness, friability, and particle size, assessing active ingredient concentration and impurities, pH Testing to determine acidity or alkalinity, impacting stability and effectiveness and Moisture Content Analysis for evaluating moisture levels to ensure stability and shelf life.
Microbiological Laboratory Tests
Assesses the number of microorganisms in non-sterile products, such as tablets and syrups, to ensure they are within acceptable limits. Endotoxin testing detects bacterial endotoxins in products, particularly important for parenteral drugs, using methods like the LAL test. Preservative Efficacy Testing evaluates effectiveness of preservatives in preventing microbial growth over time.
Packaging Material Laboratory Tests
Tests the quality and suitability of packaging materials used to contain and protect pharmaceutical products. Barrier Properties Testing assesses how well packaging materials protect against environmental factors such as moisture, oxygen, and light. Compatibility Testing ensures that packaging materials do not interact adversely with the drug product. Mechanical Properties Testing tests the strength and durability of packaging materials to ensure they can withstand handling and transport.
Process Control Laboratory Tests
Focuses on monitoring and controlling various aspects of the manufacturing process to ensure consistent product quality. Process Validation ensures that manufacturing processes are capable of consistently producing products that meet specifications. Critical Parameter Monitoring tracks critical process parameters, such as temperature and mixing speed, to ensure they remain within acceptable limits. Equipment Calibration ensures that equipment used in the manufacturing process is calibrated and functioning correctly to maintain process accuracy.
Different aspects of QC Planning
Quality Control (QC) planning involves various aspects to ensure consistent quality and safety of pharmaceutical products. Key aspects include:
Developing the test protocol: Creating detailed, step-by-step instructions for conducting QC tests, including sample preparation, test conditions, and safety precautions.
Selecting appropriate test processes: Choosing validated methods that ensure accuracy, reproducibility, and suitability for the product type.
Equipment and Resource: Calibrated instruments and high-purity reagents, is crucial for accurate testing.
Personnel Training: Personnel should be well-trained and regularly assessed to maintain testing accuracy.
Validation of QC tests: Quality control tests must be validated for accuracy, precision, specificity, and robustness
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Ensures traceability and compliance
Reporting and Communication: Clear communication with stakeholders and regulatory bodies with the help of test reports
Best Practices in QC Planning & Scheduling
Understand Regulatory Requirements: Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and WHO have stringent guidelines in quality control of pharmaceutical products. Companies must ensure that their QC processes align with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other relevant regulations. Staying updated with changes in regulations and industry standards is crucial to avoid non-compliance and potential penalties.
Adopt a Risk-Based Approach: Incorporating a risk-based approach in QC planning helps prioritize testing activities based on the criticality of the processes and the potential risks involved. By identifying high-risk areas, resources can be allocated more effectively, ensuring that critical quality attributes (CQAs) and critical process parameters (CPPs) are thoroughly evaluated. This approach not only enhances the reliability of QC activities but also optimizes time and resource utilization.
Integrate QC with Production Scheduling: QC planning should not be an isolated process; it must be integrated with production scheduling. Coordination between QC and production teams ensures that testing activities are aligned with manufacturing timelines. This integration helps in avoiding bottlenecks, ensuring timely release of batches, and reducing production delays. Advanced planning tools can be utilized to synchronize QC schedules with production demands, thus enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Leverage Technology for Automation: The adoption of digital tools and automation in QC processes can significantly improve accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Implementing a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS), Quality Management System (QMS) can streamline data management, automate scheduling, and facilitate real-time tracking of QC activities. Automation reduces the chances of human error, ensures consistency in testing procedures, and provides a comprehensive audit trail for regulatory inspections.
Optimize Resource Allocation: Efficient resource allocation is vital for effective QC planning and scheduling. This includes the optimal use of laboratory personnel, equipment, and materials. Resource planning tools can help forecast demand, allocate resources based on priority, and prevent overloading of QC teams. Cross-training personnel to handle multiple QC tasks can also enhance flexibility and ensure continuity in operations during peak periods.
Implement Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Loops: Continuous monitoring of QC processes and schedules is essential for identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Implementing feedback loops allows for real-time adjustments to be made to the schedule, ensuring that any deviations are promptly addressed. Regular reviews of QC performance metrics, such as turnaround time and first-pass yield, can help in refining planning and scheduling strategies, ultimately leading to improved product quality and compliance.
Ensure Effective Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication between QC, production, procurement, and regulatory teams is crucial for successful QC planning and scheduling. Regular meetings, transparent reporting, and collaborative decision-making processes help in aligning objectives and resolving any issues that may arise during the implementation phase. Establishing clear communication channels ensures that all stakeholders are informed of the QC schedule and any changes that may impact production timelines.
Plan for Contingencies: In the pharmaceutical industry, unexpected challenges such as equipment failure, supply chain disruptions, or sudden regulatory changes can impact QC activities. It is essential to have contingency plans in place to address these challenges. This may include maintaining backup equipment, having alternative suppliers, or pre-scheduling additional QC slots to accommodate unforeseen delays. A proactive approach to contingency planning ensures that QC processes remain robust and adaptable to changing circumstances.
Focus on Continuous Improvement: QC planning and scheduling should not be static. Continuous improvement through regular assessments, benchmarking against industry standards, and incorporating feedback from QC teams can lead to better outcomes. Embracing a culture of continuous improvement encourages innovation, enhances efficiency, and ensures that the QC processes remain aligned with evolving industry needs.
Training and Development: Finally, investing in the training and development of QC personnel is critical for maintaining high standards in QC planning and scheduling. Regular training sessions on new technologies, regulatory updates, and best practices ensure that the QC team is equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their tasks efficiently. A well-trained team is better positioned to handle complex QC activities, adapt to new challenges, and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Implementing effective QC planning and scheduling in the pharmaceutical industry is a complex but essential process. By following the above-mentioned best practices, organizations can enhance efficiency and reliability of their QC operations, ensuring that they consistently deliver high-quality products that meet regulatory standards.